HDF5 Stackable Virtual File Driver
(Rev:
HDF5 currently has an internal "Virtual File Driver" (VFD) abstraction layer through which it performs I/O on a file. However, the VFDs implemented in the library currently perform two different functions, limiting their ability to perform certain operations.
One set of VFDs in the library don't actually perform I/O, they instead perform various "logical" partitioning of the data in the file (such as sending all the metadata to one file and all the raw data to another file) and then are hard-wired to perform I/O using a specific set of I/O calls. The other set of VFDs in the library perform physical I/O on a file (or proxy for a file, such as a memory image of a file or a network socket).
It would be very advantageous to allow "logical" VFDs in the HDF5 library to stack on different "physical" VFDs to perform their actual I/O. Additionally, this should allow new VFDs to be developed with less cost and code duplication, as they would be able to address specific logical or physical I/O issues without mixing the two domains together.
HDF5 Stackable
Virtual File Driver
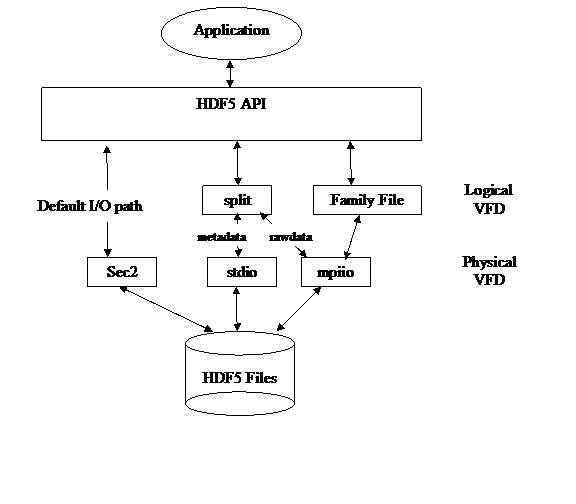
Examples of current implementation:
· The 'split file' VFD puts all metadata in one file and all raw data in another file, but is hard-coded to use the stdio routine to perform actual I/O on the file:
split
+--stdio (meta)
+--stdio (raw)
· The 'mpio' VFD enforces parallel HDF5 restrictions on metadata coherency, but is hard-coded to always use MPI-I/O for file I/O:
mpio = phdf5+mpiio (meta & raw)
Some examples of what would be possible under the revised design:
· A replacement for the current 'mpio' driver, which separated the parallel HDF5 metadata coherency constraints from the physical I/O driver, using two VFDs:
phdf5
+--mpiio
· A stack of drivers that enforced PHDF5 semantics on file accesses, while storing metadata and raw data in separate files. The metadata file, tend to have small sizes I/O, can be stored on a regular Unix file system while the raw data file, tend to have large size I/O, can be store on the parallel file system. This split arrangement can provide improved I/O according to I/O sizes characteristics.
phdf5
+--split
+--stdio (meta)
+--mpiio (raw)